Content
- The Audit Risk Formula includes a self-study e-book delivered to you immediately upon purchase for 3.5 hours of CPE credit.
- What is Audit Risk?
- Intelligent Rebate Management Solution
- Operational risk analysis in business processes using decomposed fuzzy sets
- Audit Risk Components
- The Audit Risk Formula
- Risk of Material Misstatement Formula
It is also more likely when significant estimates must be included in transactions, where an estimation error can be made. Inherent risk is also more likely when the transactions in which a client engages are highly complex, and so are more likely to be completed or recorded incorrectly.
- Inherent risk and control risk make up the risk of material misstatement formula.
- The auditor should apply analytical procedures at the planning stage, throughout the audit and at the overall review stage of the audit.
- Suggest circumstances or factors that would cause you to believe that the level of inherent risk attaching to your client was higher than usual.
- For the last thirty years, he has primarily audited governments, nonprofits, and small businesses.
- They’ll also need to look at external factors like government policy and market conditions, as well as financial performance and management strategies.
- Detection risk , the probability that the auditing procedures may fail to detect existence of a material error or fraud.
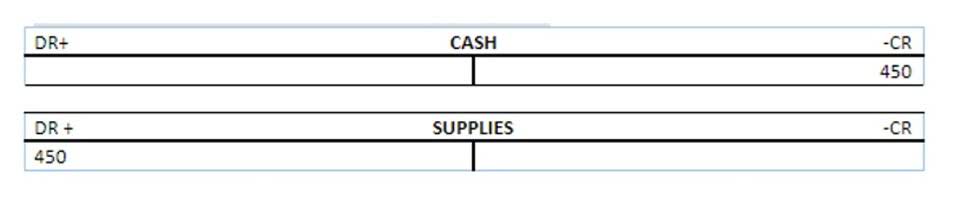
- The accountant may be inefficient or competent and may recognise the total amount of the government grants as income in the year 1’s financial statements.
Detection risk is one of three elements that comprise audit risk, the other two being inherent risk and control risk. Detection risk is the chance that an auditor will not find material misstatements relating to an assertion in an entity’s financial statements through substantive tests and analysis. Audit risk models are used during the planning stages of an audit to help the team determine which procedures make the most sense.
The Audit Risk Formula includes a self-study e-book delivered to you immediately upon purchase for 3.5 hours of CPE credit.
Next Professor Crockett explains audit procedures appropriate for securing evidence and the weights that should be assigned to the various types of evidence. This base of knowledge allows the Professor to explain the evidence terminology and formulas promulgated by the AICPA. Charles Hall is a practicing CPA and Certified Fraud Examiner. For the last thirty years, he has primarily audited governments, nonprofits, and small businesses. He is the author of The Little Book of Local Government Fraud Prevention and Preparation of Financial Statements & Compilation Engagements. Charles is the quality control partner for McNair, McLemore, Middlebrooks & Co. where he provides daily audit and accounting assistance to over 65 CPAs. In addition, he consults with other CPA firms, assisting them with auditing and accounting issues.
On the other hand, RBA also positively and significantly affect to quality of independent audit firms. Finally, some recommendations were proposed based on the results of influent factors. In the risk model, audit risk is usually set at a low level of 5% (i.e. 95% confidence that the financial statements do not contain any material misstatements).
What is Audit Risk?
Identify the inherent risks that may arise and suggest appropriate controls to reduce the impact of these risks. Risk that the auditor or audit firm will suffer harm after audit completion even though audit was conducted correctly. Such as if the co. declares bankruptcy after there is a high likelihood of the CPA firm being sued even if the audit quality was high.
How do you calculate audit risk percentage?
- Audit risk = inherent risk x control risk x detection risk.
- Audit risk = risk of material misstatement x detection risk.
- Financial Navigation is an audit firm hired to audit a company called Plugged-In Investments.
The more internal control that your organisation is able to manage, the lower your audit risk will be. It’s also possible to think of the audit risk formula as the relationship between https://www.bookstime.com/ the risk of material misstatement and detection risk. A risk assessment is necessary so that auditors can set tolerable acceptance levels for detection risk accordingly.
Intelligent Rebate Management Solution
Creditors, shareholders, and stakeholders rely on financial statements to make informed decisions when it comes to investments. Often issued quarterly, financial statements provide insights into the financial health of a company or business. audit risk model Public companies are required by law to have independent audit firms audit their books of accounts from time to time. In the process of preparing the financial statements, irregularities often occur, leading to what is termed as audit risk.
The more complex business transactions are, the higher the inherent risk the client will have. With this, the auditor checks the arithmetic accuracy of transactions in the financial statements as well as other documents such as invoices among others. The auditors should apply analytical procedures at the planning stage to assist in understanding the entity’s business and in identifying areas of potential risk.
Operational risk analysis in business processes using decomposed fuzzy sets
This study considers factors affecting to audit performance by risk-based approach as well as audit quality in Vietnam. In addition, the study also examines the relationship between RBA and quality of independent audit firms.